| 1. | EXECUTIVE SUMMARY |
| 1.1. | Executive introduction |
| 1.1.1. | How can mobile robots be used in logistics? |
| 1.1.2. | Major impact factors for the current market of logistics mobile robots |
| 1.1.3. | Major impact factors for the current market of logistics mobile robots |
| 1.1.4. | Sales leap in 2022 |
| 1.1.5. | Forecast summary - mobile robots excluding L4 trucks |
| 1.1.6. | Forecast summary - heavy-duty L4 trucks |
| 1.1.7. | Forecast numbers - intralogistics transporting robots |
| 1.1.8. | Forecast numbers - other products and the sum of market revenue |
| 1.2. | Chapter-by-chapter findings, analysis and conclusions |
| 1.3. | Intralogistics material transporting |
| 1.3.1. | Different types of mobile robotics in material handling |
| 1.3.2. | Different types of mobile robots in intralogistics material transporting |
| 1.3.3. | Mobile robots vs. fixed automation |
| 1.3.4. | Market outlook for intralogistics material transporting robots |
| 1.4. | Mobile picking |
| 1.4.1. | Two forms of mobile picking robots on the current market |
| 1.4.2. | Market outlook for mobile picking robots |
| 1.5. | Level-4 autonomous trucking |
| 1.5.1. | Market outlook for heavy-duty level-4 autonomous trucks |
| 1.6. | Last-mile delivery |
| 1.6.1. | Why autonomous last mile delivery? |
| 1.6.2. | Market outlook for last mile delivery robots and drones |
| 2. | MOBILE ROBOTICS IN LOGISTICS: OVERVIEW AND INTRODUCTION |
| 2.1. | What are mobile robots? |
| 2.2. | Why mobile robots? |
| 2.3. | How can mobile robots be used in logistics? |
| 2.4. | SLAM |
| 2.5. | Typical sensors for object detection |
| 2.6. | Major impact factors for the current market of logistics mobile robots |
| 2.7. | Labour shortage |
| 2.8. | E-commerce |
| 2.9. | Chip shortage |
| 2.10. | COVID impact |
| 2.11. | Sales leap in 2022 |
| 2.12. | Robot-as-a-Service (RaaS) |
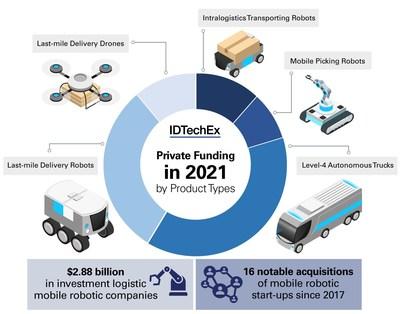
| 2.13. | Funding trending |
| 2.14. | Acquisition |
| 2.15. | Methodology and assumptions for forecasts |
| 2.16. | Illustration of S-curve |
| 3. | INTRALOGISTICS MATERIAL TRANSPORTING MOBILE ROBOTS |
| 3.1.1. | Different types of mobile robotics in material handling |
| 3.1.2. | Different types of mobile robots in intralogistics material transporting |
| 3.1.3. | Automated Guide Vehicles & Carts (AGV/Cs) |
| 3.1.4. | Grid-based automated guided carts (grid-based AGC) |
| 3.1.5. | Autonomous Mobile Robots(AMRs) |
| 3.2. | Comparison of technologies |
| 3.2.1. | Transition to AGVs and AMRs |
| 3.2.2. | Mobile robots vs. fixed automation |
| 3.2.3. | Why use mobile robots in warehouses? |
| 3.2.4. | AGV/Cs vs. AMRs |
| 3.2.5. | Technology evolution towards fully autonomous independent mobile robots |
| 3.3. | Players |
| 3.3.1. | Players - Region |
| 3.3.2. | Players - Funding |
| 3.3.3. | Players - Leading Companies for AGVs |
| 3.3.4. | AGV companies: partnership with forklift companies |
| 3.3.5. | Players - Leading Companies for grid-based AGC |
| 3.3.6. | Players - Leading Companies for AMR |
| 3.4. | Forecasts |
| 3.4.1. | Forecast - market size by product types |
| 3.4.2. | Forecast - Forklift and tow tractor AGVs |
| 3.4.3. | Forecast - Unit load and other AGVs |
| 3.4.4. | Forecast - Grid-based AGC |
| 3.4.5. | Forecast - Grid-based AGC |
| 3.4.6. | Other forms of goods-to-person robot |
| 3.4.7. | Forecast - Unit load AMR, Heavy-load AMV, other material transporting AMR |
| 3.4.8. | Toc for examples |
| 3.5. | Examples of AGVs |
| 3.5.1. | Toyota Material Handling |
| 3.5.2. | Dematic |
| 3.5.3. | ASTI: acquired by ABB in July 2021 |
| 3.5.4. | Linde |
| 3.5.5. | Daifuku |
| 3.5.6. | SSI Scheafer |
| 3.5.7. | Murata Machinery |
| 3.5.8. | Swisslog |
| 3.5.9. | Multiway |
| 3.5.10. | America in Motion |
| 3.6. | Examples of grid-based AGCs |
| 3.6.1. | Amazon Robotics (formerly Kiva) |
| 3.6.2. | Amazon Robotics (formerly Kiva) |
| 3.6.3. | Geek+ |
| 3.6.4. | Hikrobot |
| 3.6.5. | GreyOrange |
| 3.6.6. | Swisslog |
| 3.6.7. | Quicktron |
| 3.6.8. | Prime Robotics |
| 3.6.9. | Malu Innovation |
| 3.6.10. | Scallog |
| 3.7. | Examples of AMRs |
| 3.7.1. | Omron |
| 3.7.2. | SeeGrid |
| 3.7.3. | Mobile Industrial Robots (MiR) |
| 3.7.4. | Locus Robotics |
| 3.7.5. | Fetch Robotics |
| 3.7.6. | ForwardX Robotics |
| 3.7.7. | Standard Robots |
| 3.7.8. | Milvus Robotics |
| 3.7.9. | 6 River Systems |
| 3.7.10. | Honeywell Intelligrated |
| 3.7.11. | KNAPP |
| 3.7.12. | Otto Motors |
| 3.7.13. | Syrius Robotics |
| 4. | MOBILE PICKING ROBOTS |
| 4.1.1. | Two forms of mobile picking robots on the current market |
| 4.1.2. | Case-picking robots |
| 4.1.3. | Comparison: grid-based AGCs and multi-layer case-picking robots |
| 4.1.4. | Navigation technologies of case-picking robots |
| 4.1.5. | Mobile manipulators |
| 4.1.6. | Manipulator picking algorithm evolution |
| 4.2. | Players |
| 4.2.1. | Players - case-picking mobile robots |
| 4.2.2. | Players - mobile picking manipulators |
| 4.2.3. | Hybrid mobile manipulator |
| 4.3. | Forecasts |
| 4.3.1. | Forecasts |
| 4.3.2. | Forecasts - case-picking robots |
| 4.3.3. | Forecasts - mobile picking manipulators |
| 4.3.4. | Toc of examples |
| 4.4. | Examples of case-picking robots |
| 4.4.1. | HAI Robotics |
| 4.4.2. | Geek+ |
| 4.4.3. | Exotec Systems |
| 4.4.4. | InVia Robotics |
| 4.4.5. | Magazino |
| 4.4.6. | BionicHive |
| 4.4.7. | Caja Robotics |
| 4.5. | Examples of mobile picking manipulators |
| 4.5.1. | IAM Robotics |
| 4.5.2. | IAM Robotics |
| 4.5.3. | Fetch Robotics |
| 4.5.4. | Youibot |
| 5. | HEAVY-DUTY LEVEL-4 AUTONOMOUS TRUCKS |
| 5.1.1. | Pain points in the trucking industry |
| 5.1.2. | Why autonomous trucks? |
| 5.1.3. | SAE levels of automation |
| 5.1.4. | Level-2 and level-4 trucking |
| 5.1.5. | Level-4 MaaS for trucking |
| 5.1.6. | Authorities for regulating autonomous driving |
| 5.1.7. | The Autonomous Legal Race |
| 5.2. | Players |
| 5.2.1. | Funding |
| 5.2.2. | Players |
| 5.2.3. | Market readiness level of L4 autonomous truck companies |
| 5.3. | Forecasts |
| 5.3.1. | Forecast |
| 5.3.2. | ToC of examples |
| 5.4. | Examples of level-4 autonomous trucking companies |
| 5.4.1. | TuSimple |
| 5.4.2. | TuSimple's AFN |
| 5.4.3. | TuSimple's unique perception solution |
| 5.4.4. | Perception system of TuSimple's autonomous trucks |
| 5.4.5. | TuSimple's enhanced night vision camera system |
| 5.4.6. | World's first fully autonomous semi-truck operating on public roads without human intervention |
| 5.4.7. | Embark |
| 5.4.8. | Embark: sensors |
| 5.4.9. | Einride |
| 5.4.10. | Einride: a closer look into the T-pod and E-truck |
| 5.4.11. | Einride: sensors of T-pod |
| 5.4.12. | Kodiak Robotics |
| 5.4.13. | Plus.ai |
| 5.4.14. | FABU |
| 5.4.15. | Volvo Truck |
| 5.4.16. | Daimler |
| 5.4.17. | Waymo Driver in autonomous trucks |
| 5.4.18. | Hyundai catching up in the autonomous trucking race |
| 6. | AUTONOMOUS LAST MILE DELIVERY |
| 6.1.1. | What is last mile delivery? |
| 6.1.2. | Last mile delivery: the most expensive part |
| 6.1.3. | Why autonomous last mile delivery? |
| 6.1.4. | Supporting infrastructures |
| 6.1.5. | How warehouse infrastructures goes de-centralized to adapt to e-commerce needs? |
| 6.1.6. | "Last metre" delivery: robot delivery to doorsteps |
| 6.1.7. | How can the items be autonomously delivered in last mile? |
| 6.1.8. | Comparison: ground-based vehicles vs. drones |
| 6.1.9. | Comparison: ground-based vehicles vs. drones |
| 6.2. | Technologies |
| 6.2.1. | Technologies for ground-based delivery vehicles: sensors |
| 6.2.2. | Technologies for ground-based delivery vehicles: localisation and mapping |
| 6.2.3. | Technologies for ground-based delivery vehicles: vehicle connection |
| 6.2.4. | Technologies for ground-based delivery vehicles: teleoperation and cyber security |
| 6.2.5. | Technologies for ground-based delivery vehicles: restrictions |
| 6.2.6. | Technologies for drones: two forms of designs |
| 6.2.7. | Technologies for drones: sensors |
| 6.2.8. | Technologies for drones: restrictions |
| 6.3. | Regulations |
| 6.3.1. | Regulations - for delivery vehicles |
| 6.3.2. | Regulation recent updates - for delivery vehicles |
| 6.3.3. | Regulation - for delivery drones |
| 6.3.4. | Regulation recent updates - for delivery drones |
| 6.4. | Market players |
| 6.4.1. | Players - funding of start-ups |
| 6.4.2. | Players - number of companies: share by region |
| 6.4.3. | Players - what do they deliver now? |
| 6.4.4. | Players - autonomous delivery ground-based vehicles |
| 6.4.5. | Players - autonomous delivery drones |
| 6.4.6. | Timeline - drone delivery companies |
| 6.5. | Forecast |
| 6.5.1. | Market revenue forecasts for autonomous last mile delivery vans, sidewalk robots and drones |
| 6.5.2. | Cost comparison - employing human delivery drivers vs. ground-based autonomous delivery vans |
| 6.5.3. | Forecasts - autonomous delivery ground-based vehicles |
| 6.5.4. | Forecasts - autonomous delivery ground-based vehicles |
| 6.5.5. | Forecasts - autonomous delivery drones |
| 6.5.6. | ToC for examples |
| 6.6. | Examples of autonomous last mile delivery vans |
| 6.6.1. | Nuro |
| 6.6.2. | Neolix |
| 6.6.3. | JD.com |
| 6.6.4. | Meituan |
| 6.6.5. | Alibaba |
| 6.6.6. | Cleveron |
| 6.6.7. | Udelv |
| 6.6.8. | Refraction.ai |
| 6.7. | Examples of autonomous last mile delivery sidewalk robots |
| 6.7.1. | Starship Technologies |
| 6.7.2. | ZMP |
| 6.7.3. | Amazon |
| 6.7.4. | Kiwibot |
| 6.7.5. | Serve Robotics (formerly Postmates X) |
| 6.7.6. | Robby Technologies |
| 6.8. | Examples of autonomous last mile delivery drones |
| 6.8.1. | Amazon Prime Air: when will it be ready? |
| 6.8.2. | Zipline |
| 6.8.3. | Wing |
| 6.8.4. | Matternet |
| 6.8.5. | Flytrex |
| 6.8.6. | Wingcopter |
| 6.8.7. | Flirtey |
| 6.8.8. | Antwork |
| 7. | FORECAST SUMMARY |
| 7.1. | Overall forecasts |
| 7.1.1. | Overall forecasts - mobile robots excluding L4 trucks |
| 7.1.2. | Overall forecasts - heavy-duty L4 trucks |
| 7.1.3. | Forecast numbers - intralogistics transporting robots |
| 7.1.4. | Forecast numbers - other products and the sum of market revenue |
| 7.2. | Market revenue forecasts by product categories |
| 7.2.1. | Forecasts - AGVs |
| 7.2.2. | Forecasts - grid-based AGC |
| 7.2.3. | Forecasts - AMRs |
| 7.2.4. | Forecasts - mobile case-picking robots |
| 7.2.5. | Forecasts - mobile manipulators |
| 7.2.6. | Forecasts - heavy-duty autonomous L4 trucks |
| 7.2.7. | Forecasts - ground-based autonomous last mile delivery vehicles |
| 7.2.8. | Forecasts - autonomous last mile delivery drones |